|
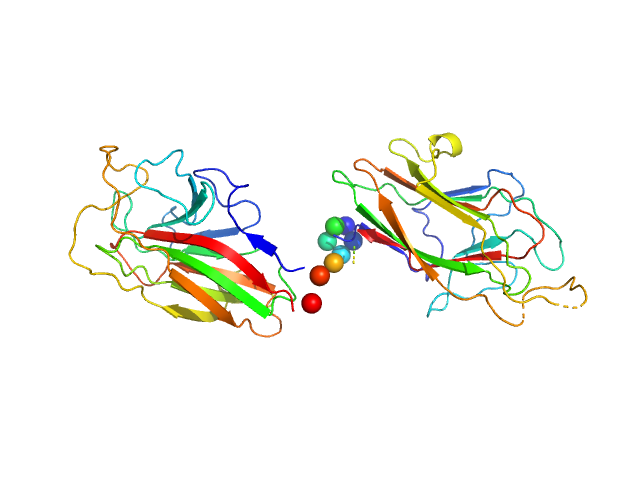
SAXS data from solutions of K1K2 domains of Kgp gingipain in 10 mM TRIS 150 mM NaCl, pH 7.6 were collected using an Anton Paar SAXSess 10 mm line collimated instrument (Sydney University, Australia) equipped with a Roper Scientific PI-SCX:4300 CCD detector at a sample-detector distance of 0.3 m and at a wavelength of λ = 0.1542 nm (I(s) vs s, where s = 4πsinθ/λ, and 2θ is the scattering angle). One solute concentration of 2.89 mg/ml was measured at 15°C. 1080 successive 10 second frames were collected. The data were normalized to the intensity of the transmitted beam and underwent 10 mm horizontal-width integration; the scattering of the solvent-blank was subtracted and the final subtracted data were desmeared.
The primary SAXS data displayed in this entry, and subsequent I(0), Rg and p(r) profile, take into account the beam-profile geometry correction (10 mm horizontal slit).
|
|
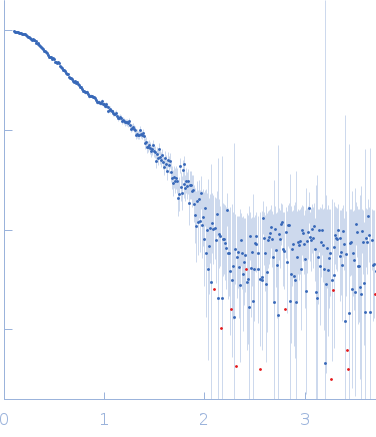 s, nm-1
s, nm-1