| MWexperimental | 67 | kDa |
| MWexpected | 62 | kDa |
|
log I(s)
1.40×10-1
1.40×10-2
1.40×10-3
1.40×10-4
|
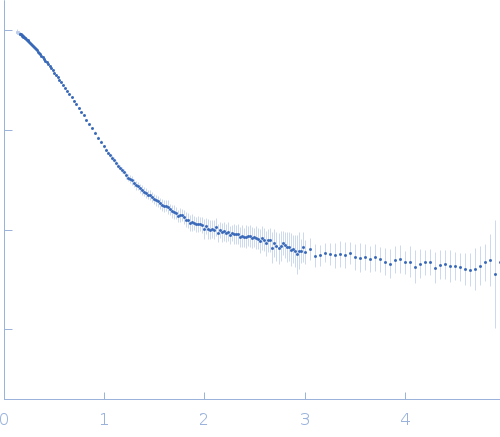 s, nm-1
s, nm-1
|
|
|
|
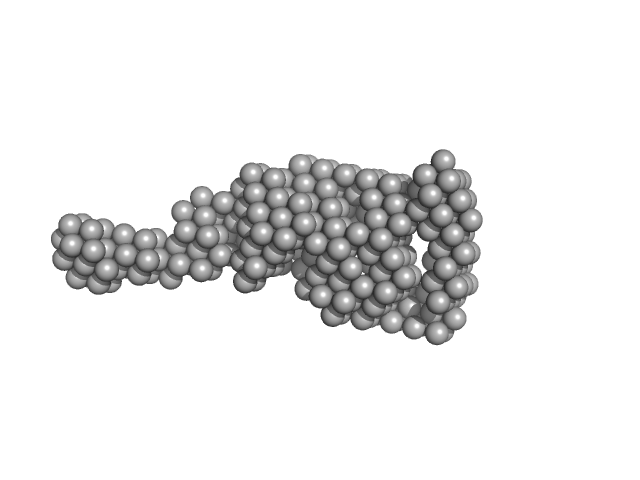
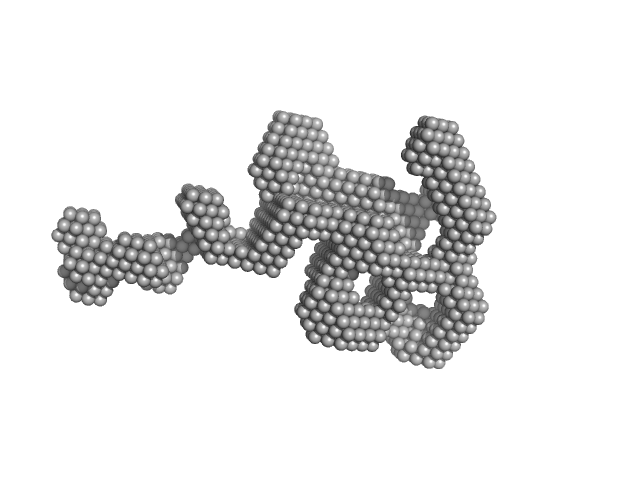
|
|
Synchrotron SAXS
data from solutions of
Human Vitamin K-dependent Activated Protein C
in
20 mM Tris, 145 mM NaCl, 5 mM CaCl2, pH 7.5
were collected
on the
12-ID-B SAXS/WAXS beam line
at the Advanced Photon Source (APS), Argonne National Laboratory storage ring
(Lemont, IL, USA)
using a Pilatus 2M detector
at a sample-detector distance of 2 m and
at a wavelength of λ = 0.09322 nm
(I(s) vs s, where s = 4πsinθ/λ, and 2θ is the scattering angle).
One solute concentration of 2.00 mg/ml was measured
at 23°C.
45 successive
0.500 second frames were collected.
The data were normalized to the intensity of the transmitted beam and radially averaged; the scattering of the solvent-blank was subtracted.
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||