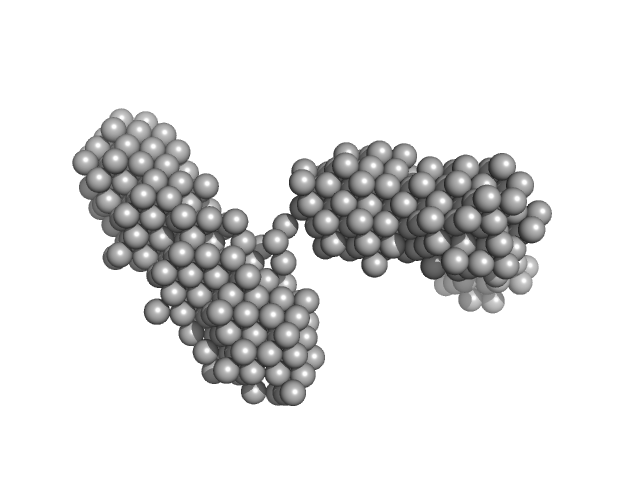|
Synchrotron SAXS
data from solutions of
LAF + P20 nanocomposite (NP added before fibrilization)
in
0.2 M glycine-HCl, 80 mM NaCl, pH 2.2
were collected
on the
EMBL P12 beam line
at the PETRA III storage ring
(DESY; Hamburg, Germany)
using a Pilatus 6M detector
at a sample-detector distance of 3 m and
at a wavelength of λ = 0.123 nm
(I(s) vs s, where s = 4πsinθ/λ, and 2θ is the scattering angle).
at 20°C.
20 successive
0.050 second frames were collected.
The data were normalized to the intensity of the transmitted beam and radially averaged; the scattering of the solvent-blank was subtracted.
LAF solution commenced with the dissolving of the hen egg white lysozyme (HEWL) powder in the buffer solution that consisted of 0.2 M glycine-HCl, with a pH of 2.2 and 80 mM NaCl, settling down at the concentration of 5 mg/mL. The buffer solution was conditioned at the acidic pH level of 2.2 for breaking down of the HEWL powder within a short period of time relative to the naturally occurring process.
Theoretical SAXS profile computed by DAMMIX analysis of a concentration series from LAF and P20 nanoparticles (in air SAXS). SVD analysis showed the presence of a third component in the mixture, which was identified as this nanocomposite.
Nanocomposite formed by addition of P20 nanoparticles BEFORE starting the LAF formation:
LAF powder solution was doped with NP of volume concentrations (10 µL, 30 µL, 300 µL), and was afterwards heated for 2 h at 65 °C while being constantly stirred at 250 rounds per minute (rpm) to form the fibrillary nanocomposites (type-B process).
|
|
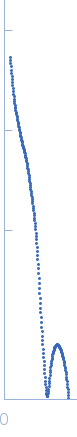 s, nm-1
s, nm-1