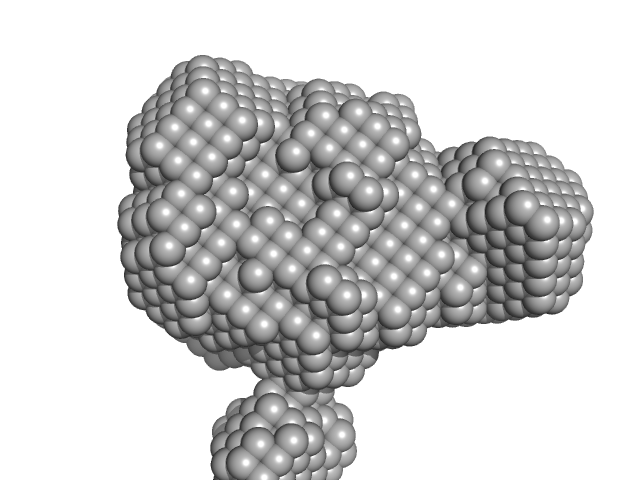
|
Synchrotron SAXS data from solutions of AT-rich DNA in 20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 200 mM NaCl, were collected on the B21 beam line at the Diamond Light Source (Didcot, UK) using a Eiger 4M detector at a sample-detector distance of 4.0 m and at a wavelength of λ = 0.1 nm (I(s) vs s, where s = 4πsinθ/λ, and 2θ is the scattering angle). In-line size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) SAS was employed. The SEC parameters were as follows: A 45.00 μl sample at 5 mg/ml was injected at a 0.10 ml/min flow rate onto a GE Superdex 200 Increase 3.2/300 column at 22°C. 619 successive 3 second frames were collected. The data were normalized to the intensity of the transmitted beam and radially averaged; the scattering of the solvent-blank was subtracted.
The ATSAS 3.0.5 suite of software was used for processing data (Manalastas-Cantos et al., 2021).
|
|
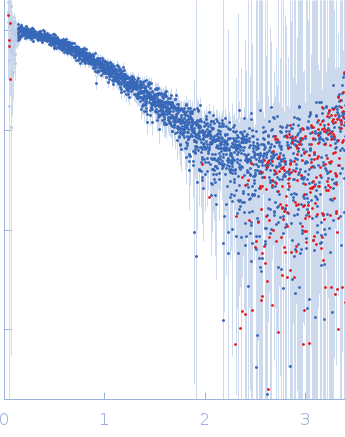 s, nm-1
s, nm-1