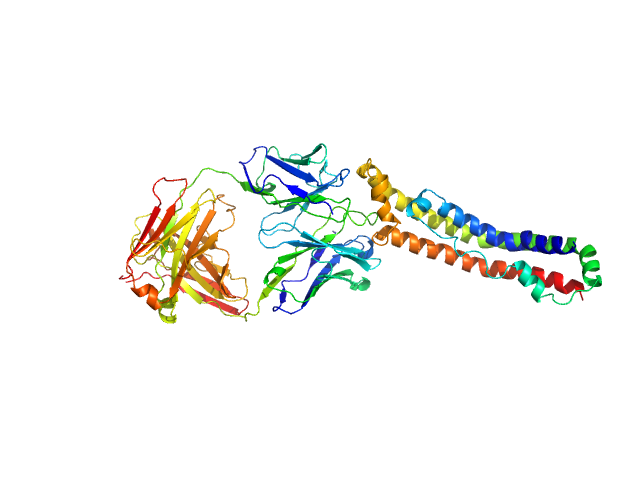
|
Synchrotron SAXS data from solutions of apolipoprotein A-I in complex with antigen-binding fragment 55201 in 20 mM Tris, 150 mM NaCl, 0.1% sodium azide, pH 7.4 were collected on the SAXS/WAXS beam line at the Australian Synchrotron (Melbourne, Australia) using a Pilatus3 S 2M detector at a wavelength of λ = 0.1078 nm (I(s) vs s, where s = 4πsinθ/λ, and 2θ is the scattering angle). One solute concentration of 7.00 mg/ml was measured at 20°C. Six successive 1 second frames were collected. The data were normalized to the intensity of the transmitted beam and radially averaged; the scattering of the solvent-blank was subtracted.
Sample detector distance: UNKNOWN.
|
|
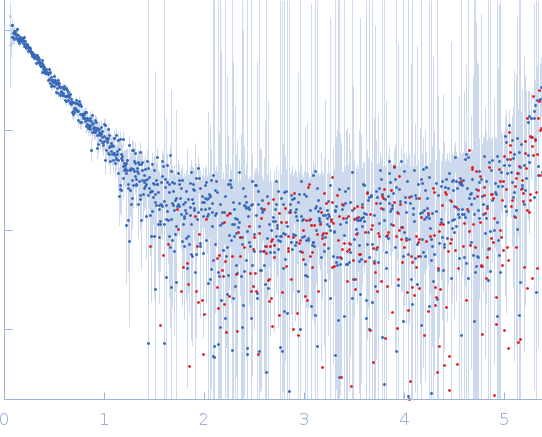 s, nm-1
s, nm-1