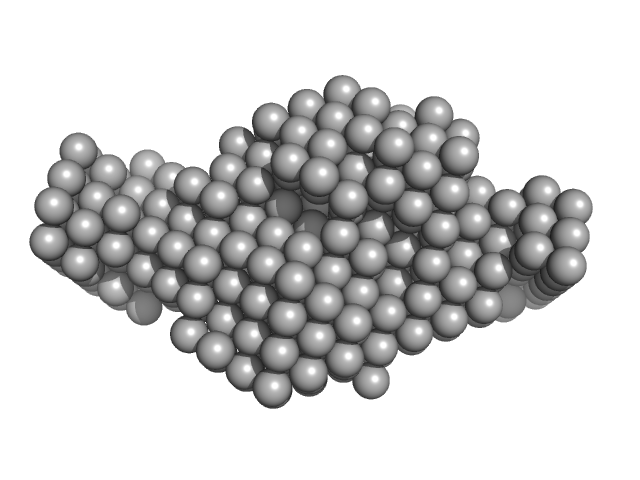
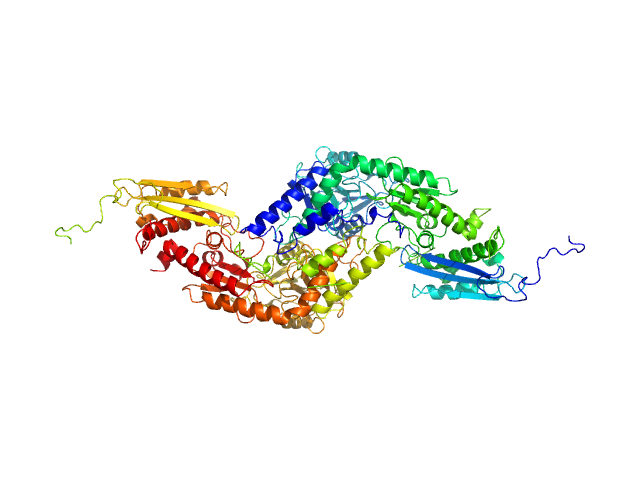
|
Synchrotron SAXS
data from solutions of
IcsS-dimer and IscU-dimer complex
in
20 mM Tris-HCl 150 mM NaCl 10 mM β-mercaptoethanol, pH 8
were collected
on the
EMBL X33 beam line
at the DORIS III, DESY storage ring
(Hamburg, Germany)
using a Pilatus 1M-W detector
at a sample-detector distance of 2.7 m and
at a wavelength of λ = 0.15 nm
(I(s) vs s, where s = 4πsinθ/λ, and 2θ is the scattering angle).
One solute concentration of 5.00 mg/ml was measured
at 15°C.
Four successive
30 second frames were collected.
The data were normalized to the intensity of the transmitted beam and radially averaged; the scattering of the solvent-blank was subtracted.
Reduced levels of frataxin, an essential protein of as yet unknown function, are responsible for causing the neurodegenerative pathology Friedreich’s ataxia. Independent reports have linked frataxin to iron–sulphur cluster assembly through interactions with the two central components of this machinery: desulphurase Nfs1/IscS and the scaffold protein Isu/IscU. In this study, we use a combination of biophysical methods to define the structural bases of the
interaction of CyaY (the bacterial orthologue of frataxin) with the IscS/IscU complex. We show that CyaY binds IscS as a monomer in a pocket between the active site and the IscS dimer interface. Recognition does not require iron and occurs through electrostatic interactions of complementary charged residues. Mutations at the complex interface affect the rates of enzymatic cluster formation. CyaY binding strengthens the affinity of the IscS/IscU complex. Our data suggest a new paradigm for understanding the role of frataxin as a regulator of IscS functions.
|
|
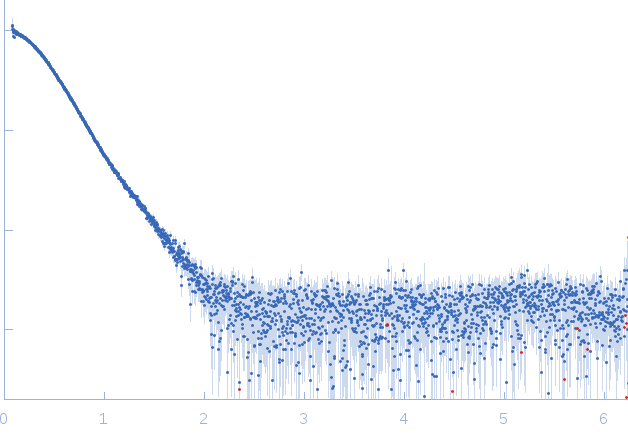 s, nm-1
s, nm-1