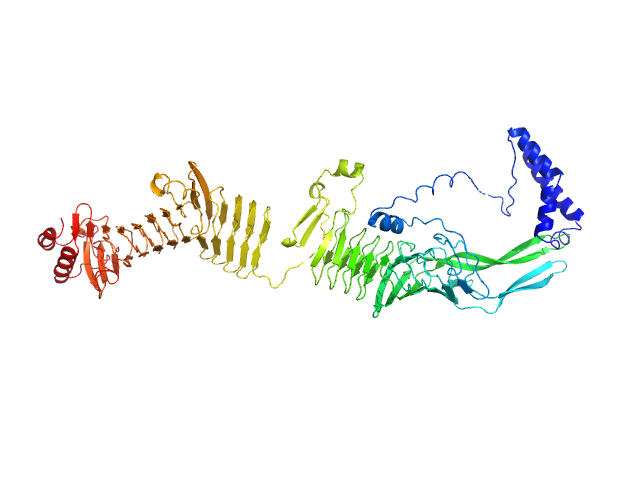
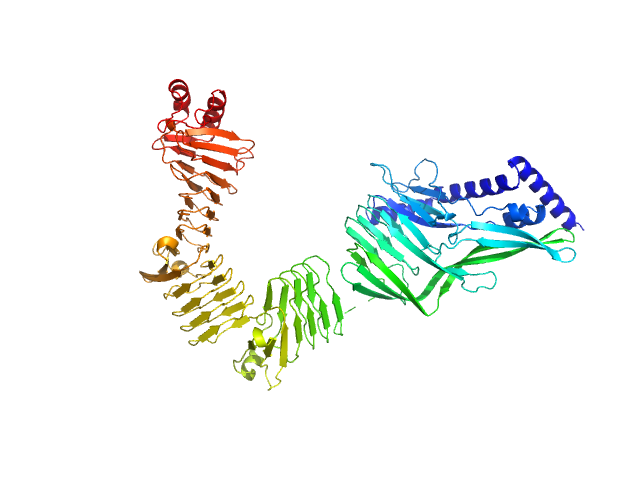
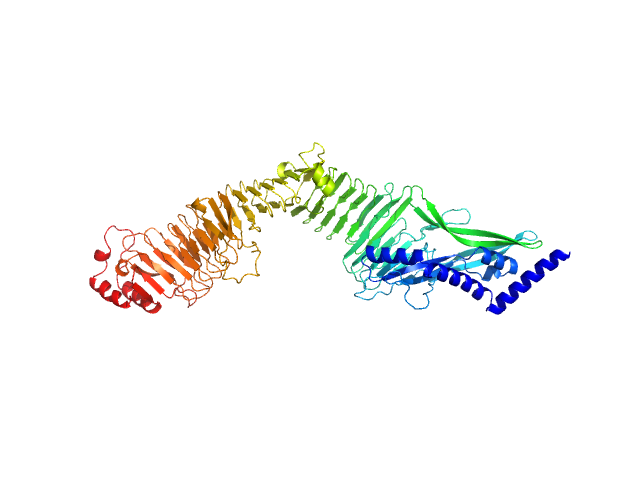
|
The SAXS measurements were done in a SAXSpoint 2.0 (Anton Paar, Graz, Austria) instrument, equipped with MetalJet C2 X-ray source (Excillum, Stockholm, Sweden) and Eiger R 1M (Dectris, Switzerland) detector. For the chromatographic separation of the oligomers and the monomeric species, an Akta GO (GE Healthcare) FPLC system with Superdex 200 Increase 10/300 column (GE Healthcare) was utilized. The chromatography was controlled automatically. The column was thoroughly equilibrated with the running buffer and the SAXS signal for buffer subtraction was also collected (2 hours) simultaneously. After loading the sample on the column, absorption of UV at 280nm was monitored (2 mm cell). Once the absorbance increased above 15 mAU, the flow rate in the system was reduced to 0.01ml/min and the sample was measured in a flow-through quartz capillary (2mm diameter), which enables in-situ UV-Vis spectroscopy using Cary 60 spectrometer (Agillent). SAXS and in-situ UV-Vis were continuously measured. The reduced scattering data was corrected to the fluctuation of primary beam, which was monitored using semi-transparent beamstop.
OVERSUBTRACTED. POTENTIALLY AGGREGATED.
|
|
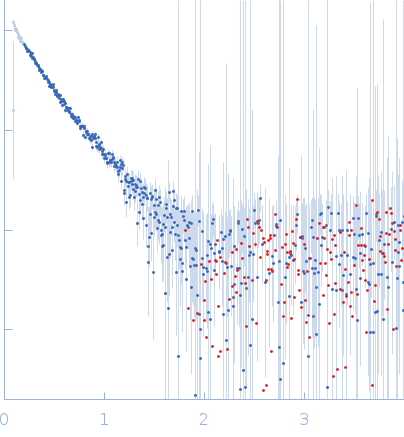 s, nm-1
s, nm-1
 Rg, nm
Rg, nm