|
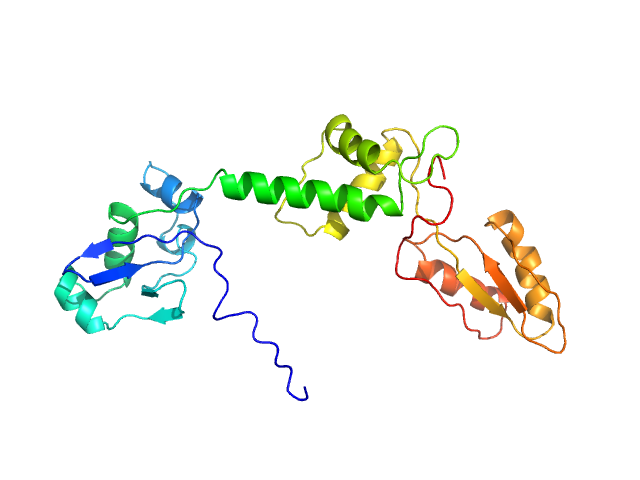
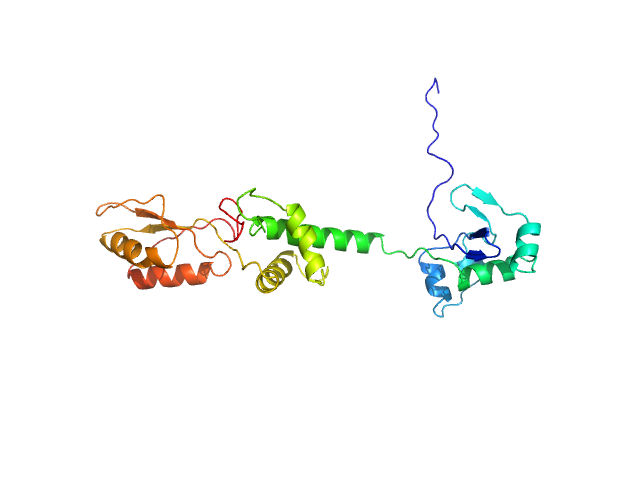
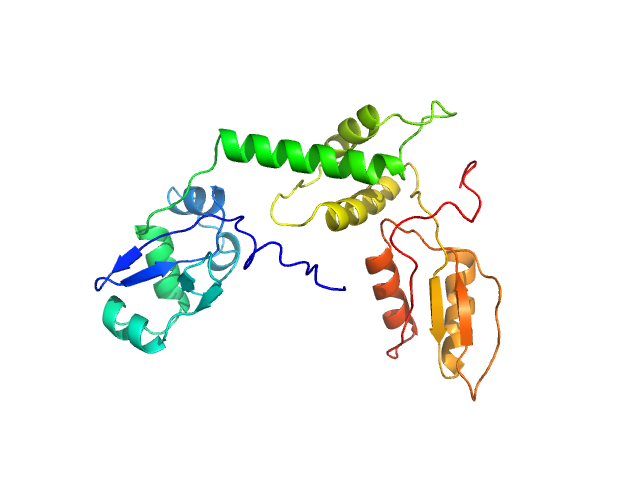
Structural characterization of human SBDS (I167T) was performed using size-exclusion chromatography coupled to small-angle X-ray scattering (SEC-SAXS), collected at the EMBL P12 beamline, at PETRA III (Hamburg, Germany), using a Pilatus 6M detector at a sample-detector distance of 3 m and at a wavelength of λ = 0.124 nm. SEC-SAXS was performed at 20° using a Superdex 75 Increase 5/150 GL size-exclusion column at a flow of 0.3 mL/min and 50 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 10% glycerol, 300 mM NaCl, and 5 mM MgCl2 as running buffer. 50 µL for the sample at concentrations of 13.8 mg/mL was injected and 1800 frames (with 0.5 s exposure time per frame) were collected. Each unsubtracted data frame was normalized to the intensity of the transmitted beam and radially averaged using integrated software available at the beamline. Chromixs software was used to select the frames corresponding to the scattering of the sample and the frames corresponding to the appropriate solvent blank. The resulting subtracted frames were scaled and averaged to generate the final SAXS profile. The flexibility study for SBDS-I167T mutant construct was performed using the online version of the program MultiFoXS, described by a 3-state model (closed, stretched and relaxt) to be compared for wt and the other mutant.
|
|
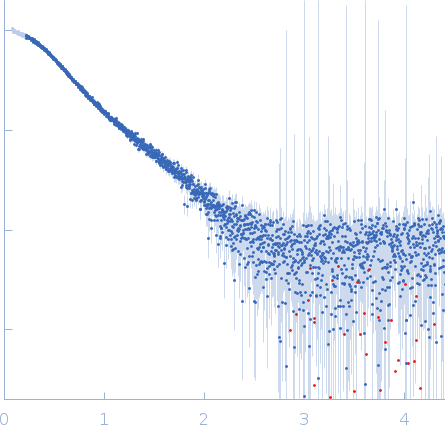 s, nm-1
s, nm-1