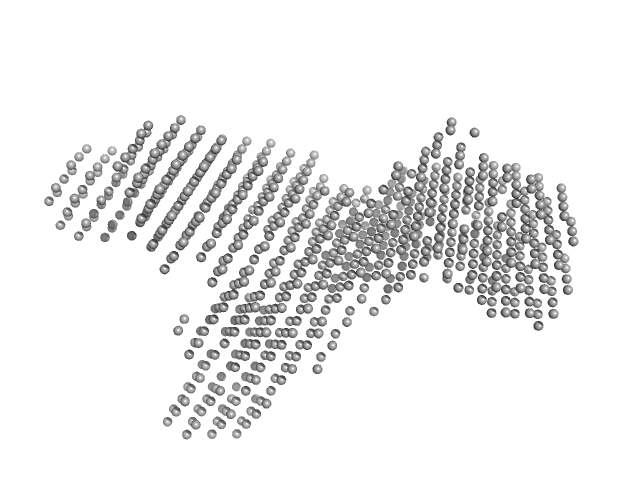
|
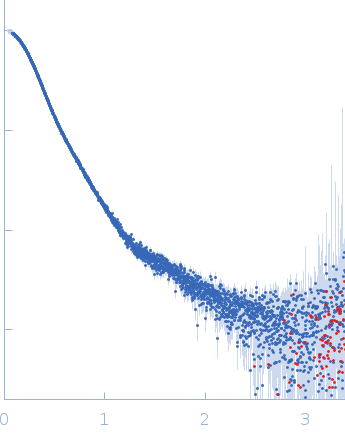
Synchrotron SAXS
data from solutions of
Mouse murine Immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies
in
20 mM Tris, 50 mM NaCl, pH 8.4
were collected
on the
B21 beam line
at the Diamond Light Source storage ring
(Didcot, UK)
using a Eiger 4M detector
at a sample-detector distance of 3.7 m and
at a wavelength of λ = 0.094 nm
(I(s) vs s, where s = 4πsinθ/λ, and 2θ is the scattering angle).
In-line size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) SAS was employed. The SEC parameters were as follows: A 50.00 μl sample
at 6.4 mg/ml was injected at a 0.07 ml/min flow rate
onto a GE Superdex 200 Increase 10/300 column
at 15°C.
620 successive
3 second frames were collected.
The data were normalized to the intensity of the transmitted beam and radially averaged; the scattering of the solvent-blank was subtracted.
Synchrotron SAXS data from solutions of murine IgE in 20 mM Tris, 50 mM NaCl, pH 8.4 were collected on the B21 beamline at Diamond (Didcot, UK) using an EigerX 4M-Detrics detector at a sample-detector distance of 3.7 m and the wavelength of 0.95 A. In-line size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) SAXS was employed. The SEC parameters were as follows: A 50.00 μl sample at 6.4 mg/ml was injected at a 0.075 ml/min flow rate onto a GE Superdex 200 Increase 10/300 column at 15°C and 620 successive 3-second frames were collected. The data were normalized to the intensity of the transmitted beam and radially averaged; the scattering of the solvent-blank was subtracted.
The molecular weight of a murine IgE, considering glycosylation, is approximately 190-198 kDa (protein 180 kDa + 10-18 kDa glycosylation). This estimate is an approximation; the actual molecular weight can vary depending on the specific glycosylation patterns and modifications of the IgE molecule.
|
|
 s, nm-1
s, nm-1
