|
Synchrotron SAXS data from solutions of Mouse complex murine Immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibody with profilin (ration 1:3) in 20 mM Tris, 50 mM NaCl, pH 8.4 were collected on the P12 beamline at the DESY (Hamburg, Germany) using a Pilatus 6M-Dectris detector at a sample-detector distance of 3.0 m and a wavelength of λ = 0.124 nm (I(s) vs s, where s = 4πsinθ/λ, and 2θ is the scattering angle). In-line size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) SAS was employed. The SEC parameters were as follows: A 50.00 μl sample at 6.0 mg/ml was injected at a 0.75 ml/min flow rate onto a GE Superdex 200 Increase 10/300 column at 15°C. 3000 successive 1.0-second frames were collected. The data were normalized to the intensity of the transmitted beam and radially averaged; the scattering of the solvent-blank was subtracted.
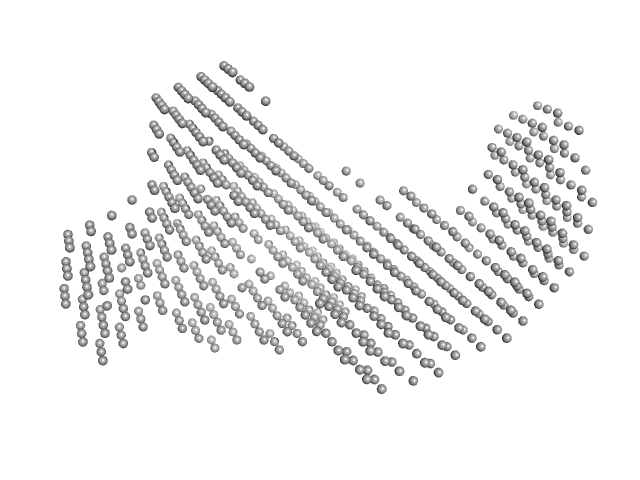
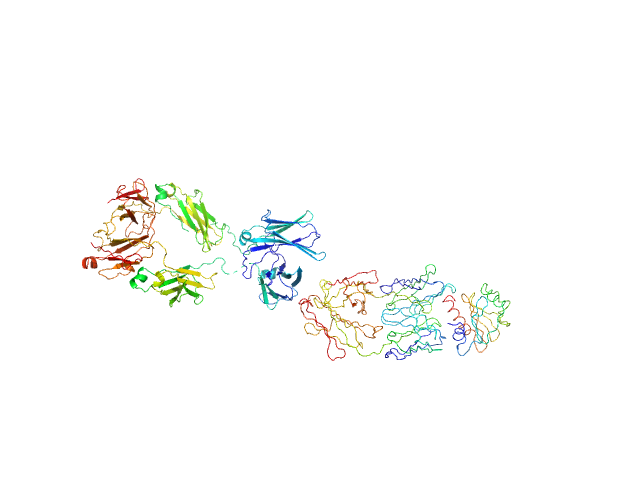
The molecular weight estimate is an approximation; the actual molecular weight can vary depending on the specific glycosylation patterns and modifications of the IgE molecule. In this way, the estimated MW for the complex (including the theProfilin) is approximately 240 kDa. For the model for IgE structure, we developed a hybrid model inspired by Jansen et al., 2020. This model incorporates two Fab regions (allergen excluded) from the crystallographic structure (PDB entry 7SBD), combined with an extended human Fc fragment (CH2-CH3-CH4) from PDB entry 4J4P. The hybrid model was manually fitted into a low-resolution SAXS envelope obtained by using the DAMMIF, DAMAVER, and DAMMIN programs (SASBDB entry SASDVG9). This model for IgE was used to generate the IgE complex with the allergen (Profilin) using crystallographic structure (PDB entry 7SBD) fitting a low-resolution SAXS envelope obtained by DAMMIN program. Further refinement of the hybrid model was conducted through Normal Mode Analysis (NMA) using the SREFLEX program based on experimental SAXS data.
|
|
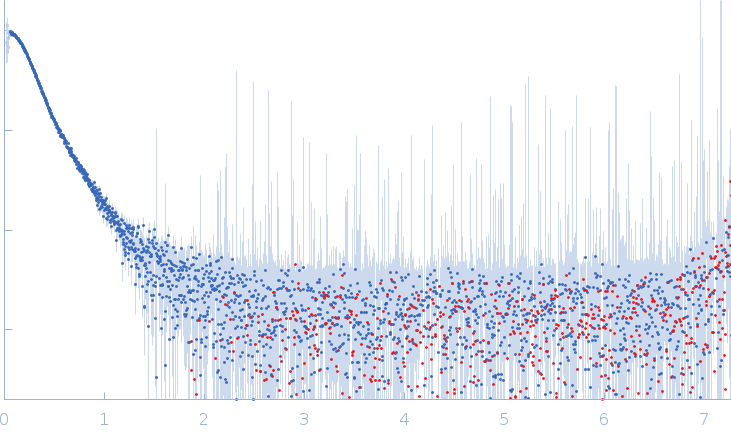 s, nm-1
s, nm-1