|
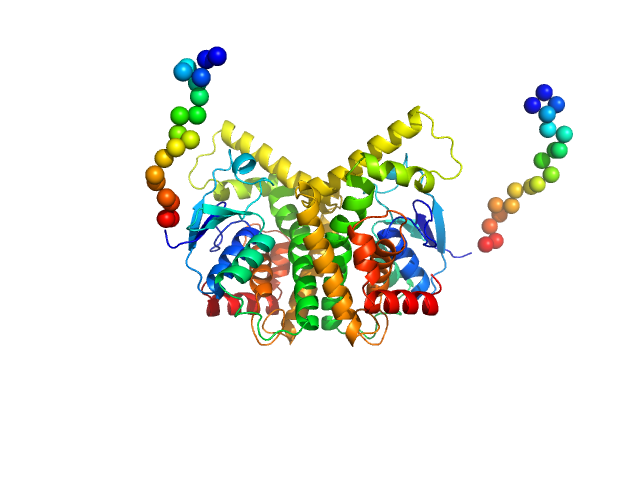
SAXS data from solutions of StyI glutathione S-transferase in 10 mM Tris, 300 mM NaCl, pH 8 were collected using a Xenocs Xeuss 2.0 Q-Zoom instrument equipped with a Pilatus3 R 300 K detector and a GENIX 3D CU Ultra Low Divergence X-ray beam delivery system (Center for Structural Studies, Heinrich-Heine-University, Düsseldorf, Germany) at a sample-detector distance of 0.6 m and at a wavelength of λ = 0.154 nm (I(s) vs s, where s = 4πsinθ/λ, and 2θ is the scattering angle). One solute concentration of 4.70 mg/ml was measured at 10°C. 12 successive 600 second frames were collected. The data were normalized to the intensity of the transmitted beam and radially averaged; the scattering of the solvent-blank was subtracted.
|
|
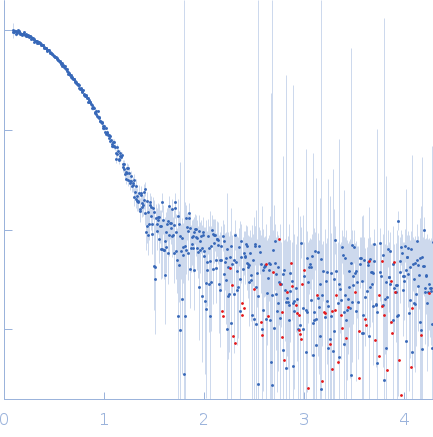 s, nm-1
s, nm-1