|
|
|
|
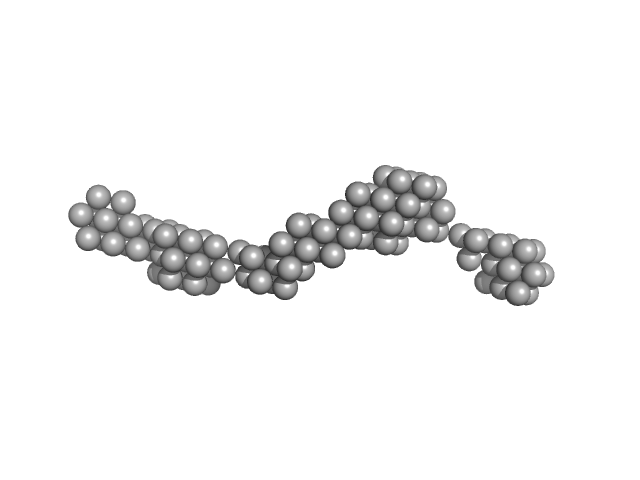
|
| Sample: |
Persulfide dioxygenase ETHE1, mitochondrial dimer, 56 kDa Homo sapiens protein
|
| Buffer: |
50 mM Tris 150 mM NaCl 2 mM TCEP, pH: 8 |
| Experiment: |
SAXS
data collected at EMBL X33, DORIS III, DESY on 2009 Nov 23
|
Distinctive features and structural significance of the Homo sapiens ethylmalonic encephalopathy protein iron binding site
Al Kikhney,
Marco Salomone-Stagni
|
| RgGuinier |
8.3 |
nm |
| Dmax |
38.0 |
nm |
| VolumePorod |
602 |
nm3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
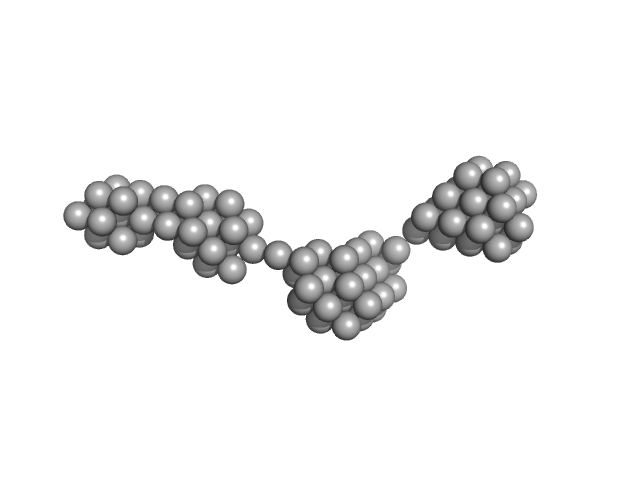
|
| Sample: |
Persulfide dioxygenase ETHE1, mitochondrial dimer, 56 kDa Homo sapiens protein
|
| Buffer: |
50 mM Tris 150 mM NaCl 2 mM TCEP, pH: 8 |
| Experiment: |
SAXS
data collected at EMBL X33, DORIS III, DESY on 2009 Nov 23
|
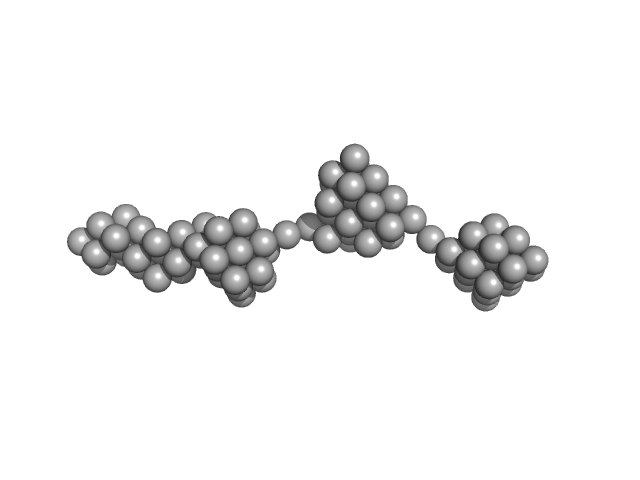
Distinctive features and structural significance of the Homo sapiens ethylmalonic encephalopathy protein iron binding site
Al Kikhney,
Marco Salomone-Stagni
|
| RgGuinier |
8.8 |
nm |
| Dmax |
42.5 |
nm |
| VolumePorod |
647 |
nm3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
| Sample: |
Persulfide dioxygenase ETHE1, mitochondrial dimer, 56 kDa Homo sapiens protein
|
| Buffer: |
50 mM Tris 150 mM NaCl 2 mM TCEP, pH: 8 |
| Experiment: |
SAXS
data collected at EMBL X33, DORIS III, DESY on 2009 Nov 23
|
Distinctive features and structural significance of the Homo sapiens ethylmalonic encephalopathy protein iron binding site
Al Kikhney,
Marco Salomone-Stagni
|
| RgGuinier |
11.2 |
nm |
| Dmax |
56.0 |
nm |
| VolumePorod |
1445 |
nm3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
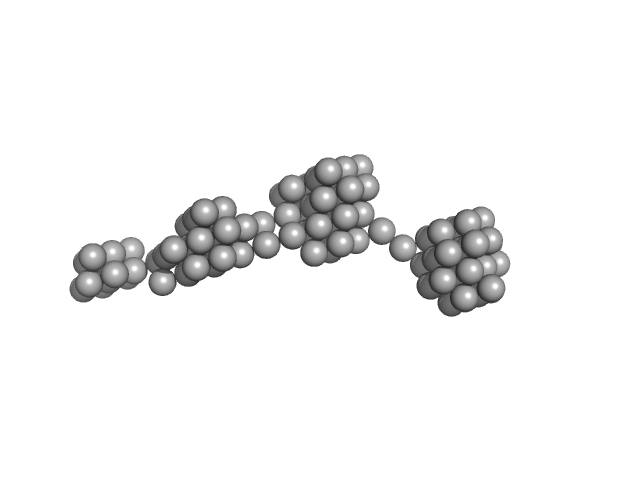
|
| Sample: |
Persulfide dioxygenase ETHE1, mitochondrial dimer, 56 kDa Homo sapiens protein
|
| Buffer: |
50 mM Tris 150 mM NaCl 2 mM TCEP, pH: 8 |
| Experiment: |
SAXS
data collected at EMBL X33, DORIS III, DESY on 2009 Nov 23
|
Distinctive features and structural significance of the Homo sapiens ethylmalonic encephalopathy protein iron binding site
Al Kikhney,
Marco Salomone-Stagni
|
| RgGuinier |
12.4 |
nm |
| Dmax |
59.0 |
nm |
| VolumePorod |
1820 |
nm3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
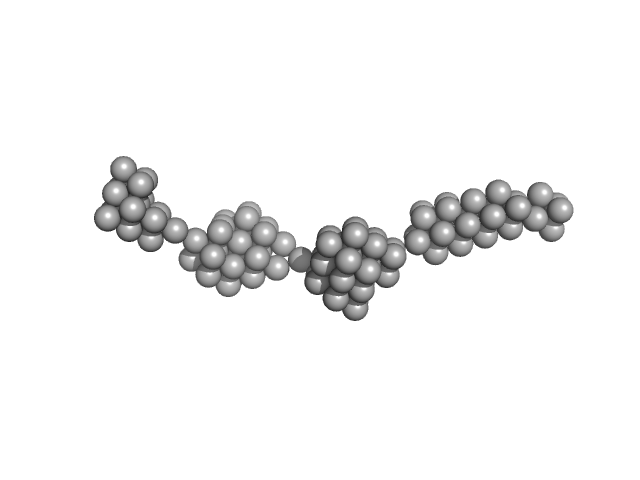
|
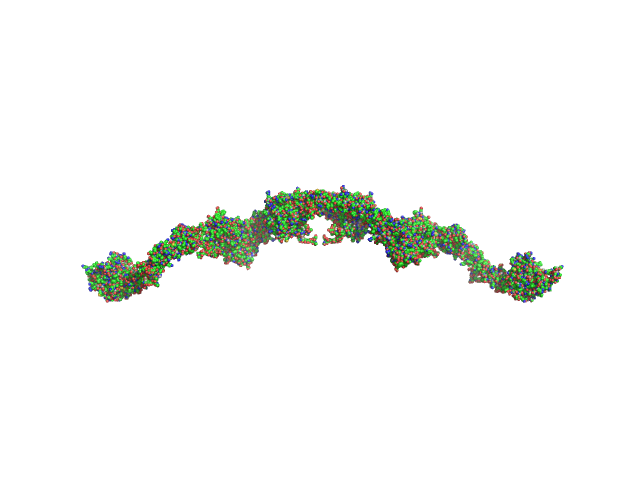
| Sample: |
Persulfide dioxygenase ETHE1, mitochondrial dimer, 56 kDa Homo sapiens protein
|
| Buffer: |
50 mM Tris 150 mM NaCl 2 mM TCEP, pH: 8 |
| Experiment: |
SAXS
data collected at EMBL X33, DORIS III, DESY on 2009 Nov 23
|
Distinctive features and structural significance of the Homo sapiens ethylmalonic encephalopathy protein iron binding site
Al Kikhney,
Marco Salomone-Stagni
|
| RgGuinier |
14.2 |
nm |
| Dmax |
63.5 |
nm |
| VolumePorod |
2317 |
nm3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Sample: |
Complement C1r subcomponent dimer, 156 kDa Homo sapiens protein
Complement C1s subcomponent dimer, 150 kDa Homo sapiens protein
|
| Buffer: |
50 mM TrisHCl, 145 mM NaCl, 3 mM CaCl2, pH: 7.4 |
| Experiment: |
SAXS
data collected at BM29, ESRF on 2014 Dec 8
|
Structure and activation of C1, the complex initiating the classical pathway of the complement cascade.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114(5):986-991 (2017)
Mortensen SA, Sander B, Jensen RK, Pedersen JS, Golas MM, Jensenius JC, Hansen AG, Thiel S, Andersen GR
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Sample: |
Complement C1q subcomponent subunit C hexamer, 142 kDa Homo sapiens protein
Complement C1q subcomponent subunit B hexamer, 142 kDa Homo sapiens protein
Complement C1q subcomponent subunit A hexamer, 142 kDa Homo sapiens protein
|
| Buffer: |
50 mM TrisHCl, 145 mM NaCl, 3 mM CaCl2, pH: 7.4 |
| Experiment: |
SAXS
data collected at BM29, ESRF on 2014 Dec 8
|
Structure and activation of C1, the complex initiating the classical pathway of the complement cascade.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114(5):986-991 (2017)
Mortensen SA, Sander B, Jensen RK, Pedersen JS, Golas MM, Jensenius JC, Hansen AG, Thiel S, Andersen GR
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
| Sample: |
Complement C1q subcomponent subunit C hexamer, 142 kDa Homo sapiens protein
Complement C1q subcomponent subunit B hexamer, 142 kDa Homo sapiens protein
Complement C1q subcomponent subunit A hexamer, 142 kDa Homo sapiens protein
Complement C1r subcomponent dimer, 156 kDa Homo sapiens protein
Complement C1s subcomponent dimer, 150 kDa Homo sapiens protein
|
| Buffer: |
50 mM EPPS, 145 mM NaCl, 3 mM CaCl2, pH: 8.5 |
| Experiment: |
SAXS
data collected at EMBL P12, PETRA III on 2015 Aug 16
|
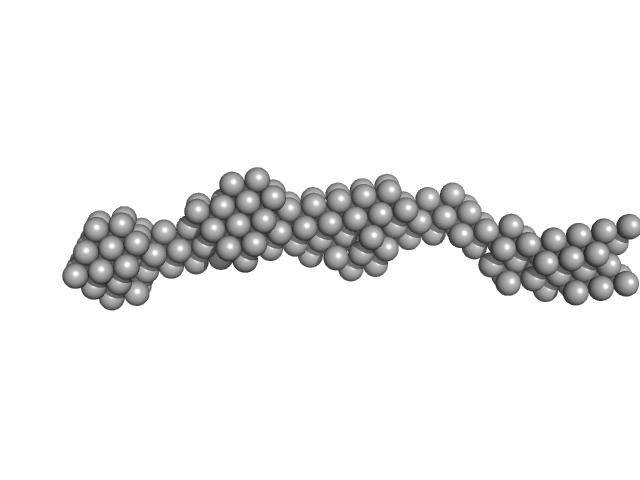
Structure and activation of C1, the complex initiating the classical pathway of the complement cascade.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114(5):986-991 (2017)
Mortensen SA, Sander B, Jensen RK, Pedersen JS, Golas MM, Jensenius JC, Hansen AG, Thiel S, Andersen GR
|
| RgGuinier |
11.5 |
nm |
| Dmax |
36.6 |
nm |
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
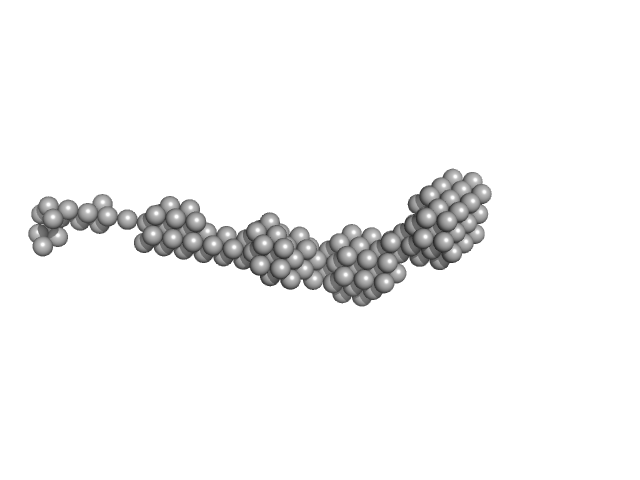
| Sample: |
Bromodomain-containing protein 4 monomer, 56 kDa Homo sapiens protein
|
| Buffer: |
20mM Hepes, 100mM NaCl, 1mM Tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine hydrochloride, pH: 7.4 |
| Experiment: |
SAXS
data collected at BM29, ESRF on 2014 Sep 12
|
Potent and selective bivalent inhibitors of BET bromodomains.
Nat Chem Biol 12(12):1097-1104 (2016)
Waring MJ, Chen H, Rabow AA, Walker G, Bobby R, Boiko S, Bradbury RH, Callis R, Clark E, Dale I, Daniels DL, Dulak A, Flavell L, Holdgate G, Jowitt TA, Kikhney A, McAlister M, Méndez J, Ogg D, Patel J, Petteruti P, Robb GR, Robers MB, Saif S, Stratton N, Svergun DI, Wang W, Whittaker D, Wilson DM, Yao Y
|
| RgGuinier |
7.0 |
nm |
| Dmax |
27.0 |
nm |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Sample: |
Bromodomain-containing protein 4 monomer, 56 kDa Homo sapiens protein
|
| Buffer: |
20mM Hepes, 100mM NaCl, 1mM Tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine hydrochloride, pH: 7.4 |
| Experiment: |
SAXS
data collected at BM29, ESRF on 2014 Sep 12
|
Potent and selective bivalent inhibitors of BET bromodomains.
Nat Chem Biol 12(12):1097-1104 (2016)
Waring MJ, Chen H, Rabow AA, Walker G, Bobby R, Boiko S, Bradbury RH, Callis R, Clark E, Dale I, Daniels DL, Dulak A, Flavell L, Holdgate G, Jowitt TA, Kikhney A, McAlister M, Méndez J, Ogg D, Patel J, Petteruti P, Robb GR, Robers MB, Saif S, Stratton N, Svergun DI, Wang W, Whittaker D, Wilson DM, Yao Y
|
| RgGuinier |
6.2 |
nm |
| Dmax |
27.5 |
nm |
|
|