|
|
|
|
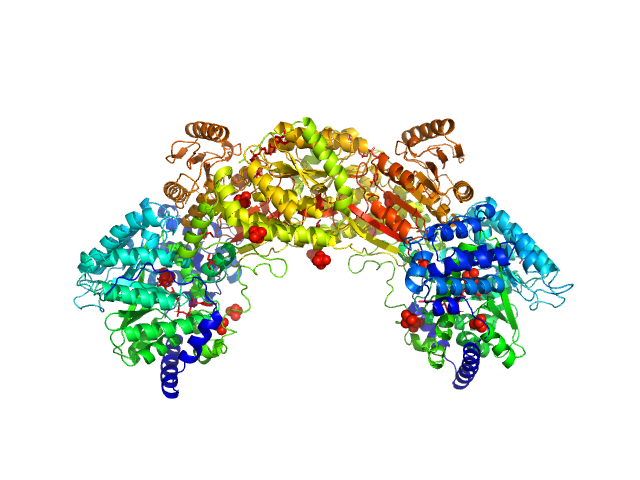
|
| Sample: |
Bifunctional protein PutA dimer, 215 kDa Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens protein
|
| Buffer: |
50 mM Tris, 50 mM NaCl, 0.5 mM TCEP, 5% (v/v) glycerol, pH: 7.8 |
| Experiment: |
SAXS
data collected at BioCAT 18ID, Advanced Photon Source (APS), Argonne National Laboratory on 2017 Jul 16
|
Redox Modulation of Oligomeric State in Proline Utilization A.
Biophys J 114(12):2833-2843 (2018)
Korasick DA, Campbell AC, Christgen SL, Chakravarthy S, White TA, Becker DF, Tanner JJ
|
| RgGuinier |
4.6 |
nm |
| Dmax |
14.4 |
nm |
| VolumePorod |
324 |
nm3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
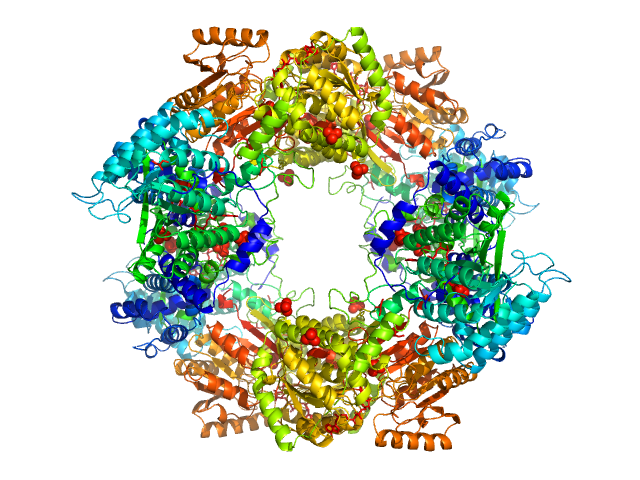
|
| Sample: |
Bifunctional protein PutA tetramer, 430 kDa Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens protein
|
| Buffer: |
50 mM Tris, 50 mM NaCl, 0.5 mM TCEP, 5% (v/v) glycerol, pH: 7.8 |
| Experiment: |
SAXS
data collected at BioCAT 18ID, Advanced Photon Source (APS), Argonne National Laboratory on 2017 Jul 16
|
Redox Modulation of Oligomeric State in Proline Utilization A.
Biophys J 114(12):2833-2843 (2018)
Korasick DA, Campbell AC, Christgen SL, Chakravarthy S, White TA, Becker DF, Tanner JJ
|
| RgGuinier |
5.2 |
nm |
| Dmax |
14.2 |
nm |
| VolumePorod |
582 |
nm3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
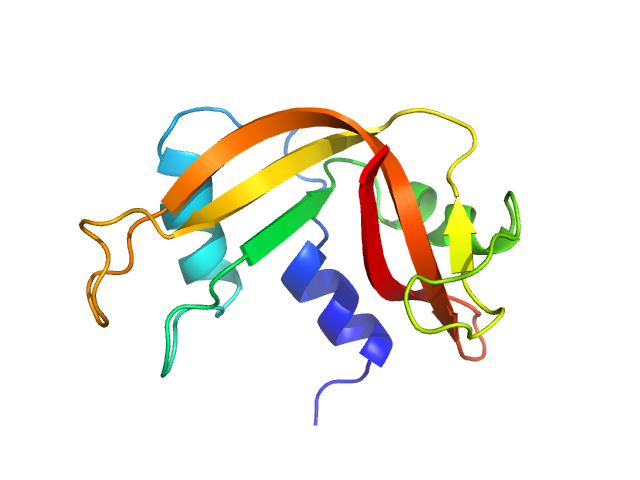
|
| Sample: |
Ribonuclease pancreatic monomer, 16 kDa Bos taurus protein
|
| Buffer: |
phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH: 7 |
| Experiment: |
SAXS
data collected at EMBL P12, PETRA III on 2013 Jul 29
|
Machine Learning Methods for X-Ray Scattering Data Analysis from Biomacromolecular Solutions.
Biophys J 114(11):2485-2492 (2018)
Franke D, Jeffries CM, Svergun DI
|
| RgGuinier |
1.6 |
nm |
| Dmax |
5.6 |
nm |
| VolumePorod |
16 |
nm3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
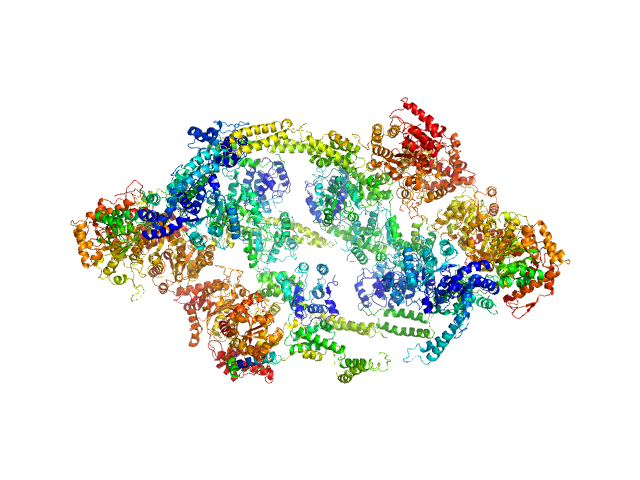
|
| Sample: |
ATP-dependent Clp protease ATP-binding subunit ClpC1, 95 kDa Mycobacterium tuberculosis protein
|
| Buffer: |
Hepes 50 mM pH 7.5, KCl 100 mM, glycerol 10%, MgCl2 4 mM and ATP 1 mM, pH: 7.5 |
| Experiment: |
SAXS
data collected at BM29, ESRF on 2017 Sep 18
|
The antibiotic cyclomarin blocks arginine-phosphate-induced millisecond dynamics in the N-terminal domain of ClpC1 from Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
J Biol Chem 293(22):8379-8393 (2018)
Weinhäupl K, Brennich M, Kazmaier U, Lelievre J, Ballell L, Goldberg A, Schanda P, Fraga H
|
| RgGuinier |
7.6 |
nm |
| Dmax |
25.0 |
nm |
| VolumePorod |
2156 |
nm3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
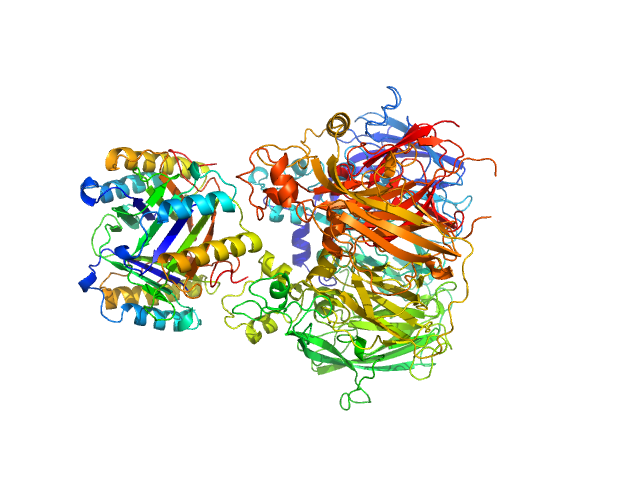
| Sample: |
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor trimer, 37 kDa Homo sapiens protein
Ceruloplasmin monomer, 122 kDa Homo sapiens protein
|
| Buffer: |
50mkm CuSO4, 100mM Hepes, pH: 7.4 |
| Experiment: |
SAXS
data collected at HECUS System-3, None on 2015 Dec 22
|
Structural Study of the Complex Formed by Ceruloplasmin and Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor.
Biochemistry (Mosc) 83(6):701-707 (2018)
Sokolov AV, Dadinova LA, Petoukhov MV, Bourenkov G, Dubova KM, Amarantov SV, Volkov VV, Kostevich VA, Gorbunov NP, Grudinina NA, Vasilyev VB, Samygina VR
|
| RgGuinier |
3.6 |
nm |
| Dmax |
14.4 |
nm |
| VolumePorod |
228 |
nm3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
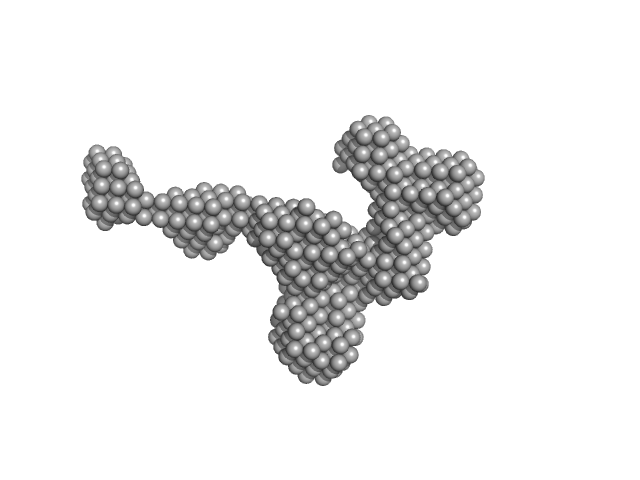
| Sample: |
Extender PN-Block (HL4) monomer, 27 kDa de novo protein protein
Stopper PN-Block (WA20) dimer, 25 kDa de novo protein protein
|
| Buffer: |
20 mM HEPES, 100 mM NaCl, 200 mM ArgHCl, 10% glycerol, pH: 7.5 |
| Experiment: |
SAXS
data collected at BL-10C, Photon Factory (PF), High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK) on 2014 Dec 19
|
Self-Assembling Supramolecular Nanostructures Constructed from de Novo Extender Protein Nanobuilding Blocks.
ACS Synth Biol 7(5):1381-1394 (2018)
Kobayashi N, Inano K, Sasahara K, Sato T, Miyazawa K, Fukuma T, Hecht MH, Song C, Murata K, Arai R
|
| RgGuinier |
3.6 |
nm |
| Dmax |
15.0 |
nm |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Sample: |
Stopper PN-Block (WA20) dimer, 25 kDa de novo protein protein
Extender PN-Block (FL4) monomer, 27 kDa de novo protein protein
|
| Buffer: |
20 mM HEPES, 100 mM NaCl, 200 mM ArgHCl, 10% glycerol, pH: 7.5 |
| Experiment: |
SAXS
data collected at BL-10C, Photon Factory (PF), High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK) on 2014 Dec 19
|
Self-Assembling Supramolecular Nanostructures Constructed from de Novo Extender Protein Nanobuilding Blocks.
ACS Synth Biol 7(5):1381-1394 (2018)
Kobayashi N, Inano K, Sasahara K, Sato T, Miyazawa K, Fukuma T, Hecht MH, Song C, Murata K, Arai R
|
| RgGuinier |
3.3 |
nm |
| Dmax |
12.0 |
nm |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
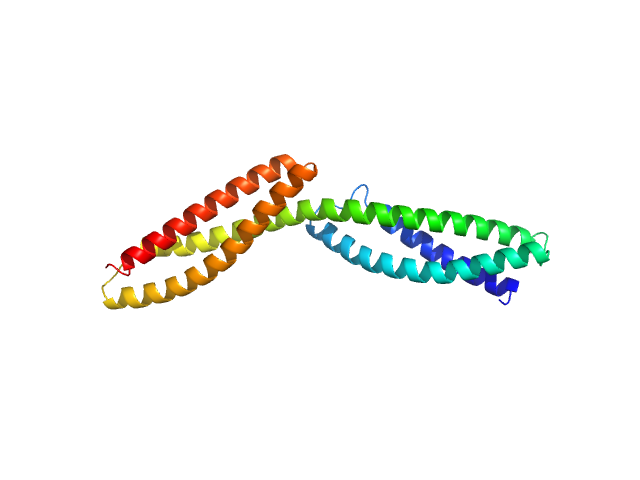
| Sample: |
Dystrophin central domain repeats 1 to 2 monomer, 26 kDa Homo sapiens protein
|
| Buffer: |
20 mM Tris 150 mM NaCl 1 mM EDTA 2% glycerol, pH: 7.5 |
| Experiment: |
SAXS
data collected at SWING, SOLEIL on 2011 Oct 7
|
Dystrophin's central domain forms a complex filament that becomes disorganized by in-frame deletions.
J Biol Chem 293(18):6637-6646 (2018)
Delalande O, Molza AE, Dos Santos Morais R, Chéron A, Pollet É, Raguenes-Nicol C, Tascon C, Giudice E, Guilbaud M, Nicolas A, Bondon A, Leturcq F, Férey N, Baaden M, Perez J, Roblin P, Piétri-Rouxel F, Hubert JF, Czjzek M, Le Rumeur E
|
| RgGuinier |
3.0 |
nm |
| Dmax |
10.6 |
nm |
| VolumePorod |
42 |
nm3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
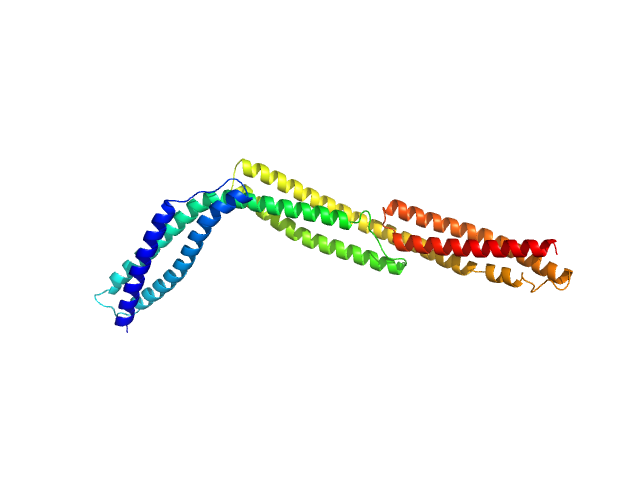
| Sample: |
Dystrophin central domain repeats 1 to 3 monomer, 38 kDa Homo sapiens protein
|
| Buffer: |
20 mM Tris 150 mM NaCl 1 mM EDTA 2% glycerol, pH: 7.5 |
| Experiment: |
SAXS
data collected at SWING, SOLEIL on 2011 Sep 9
|
Dystrophin's central domain forms a complex filament that becomes disorganized by in-frame deletions.
J Biol Chem 293(18):6637-6646 (2018)
Delalande O, Molza AE, Dos Santos Morais R, Chéron A, Pollet É, Raguenes-Nicol C, Tascon C, Giudice E, Guilbaud M, Nicolas A, Bondon A, Leturcq F, Férey N, Baaden M, Perez J, Roblin P, Piétri-Rouxel F, Hubert JF, Czjzek M, Le Rumeur E
|
| RgGuinier |
4.2 |
nm |
| Dmax |
17.0 |
nm |
| VolumePorod |
68 |
nm3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
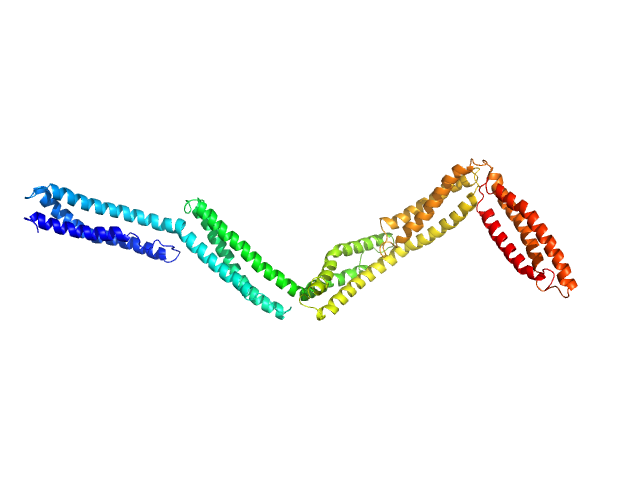
| Sample: |
Dystrophin central domain repeats 11 to 15. monomer, 60 kDa Homo sapiens protein
|
| Buffer: |
20 mM Tris 150 mM NaCl 1 mM EDTA 2% glycerol, pH: 7.5 |
| Experiment: |
SAXS
data collected at BM29, ESRF on 2011 Apr 11
|
Dystrophin's central domain forms a complex filament that becomes disorganized by in-frame deletions.
J Biol Chem 293(18):6637-6646 (2018)
Delalande O, Molza AE, Dos Santos Morais R, Chéron A, Pollet É, Raguenes-Nicol C, Tascon C, Giudice E, Guilbaud M, Nicolas A, Bondon A, Leturcq F, Férey N, Baaden M, Perez J, Roblin P, Piétri-Rouxel F, Hubert JF, Czjzek M, Le Rumeur E
|
| RgGuinier |
5.8 |
nm |
| Dmax |
23.0 |
nm |
| VolumePorod |
87 |
nm3 |
|
|